SMALLER IS BETTER?
 Peak performance requires that misfires are minimized. The diameter of the center electrode and the width of the spark plug gap influence the voltage requirements for a spark to occur. With all other factors being equal, spark plugs with smaller center electrodes will be able to generate a spark at a lower voltage than spark plugs with a larger center electrode. Smaller spark plug gaps also reduce the voltage requirements for a spark. When gaps go too small, the spark kernel may be too small to initiate combustion. Remember, spark plug electrodes will erode over time and the plug gap will increase. Don’t run a gap that’s on the edge of a misfire. When the sharp edges wear off the new plugs and erosion begins, a significant amount of misfires may result.
Peak performance requires that misfires are minimized. The diameter of the center electrode and the width of the spark plug gap influence the voltage requirements for a spark to occur. With all other factors being equal, spark plugs with smaller center electrodes will be able to generate a spark at a lower voltage than spark plugs with a larger center electrode. Smaller spark plug gaps also reduce the voltage requirements for a spark. When gaps go too small, the spark kernel may be too small to initiate combustion. Remember, spark plug electrodes will erode over time and the plug gap will increase. Don’t run a gap that’s on the edge of a misfire. When the sharp edges wear off the new plugs and erosion begins, a significant amount of misfires may result.
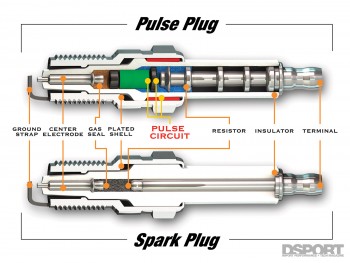 Voltage requirements are a function of gap length, electrode diameter, cylinder pressure and gas density. The bigger the spark plug gap, the higher the minimum voltage to initiate a spark. As for electrode diameter, the smaller the diameter the lower the voltage required for a spark to occur. With cylinder pressure, the higher the pressures in the cylinder (the result of high compression ratios and high boost levels), the more voltage required for a spark to occur.
Voltage requirements are a function of gap length, electrode diameter, cylinder pressure and gas density. The bigger the spark plug gap, the higher the minimum voltage to initiate a spark. As for electrode diameter, the smaller the diameter the lower the voltage required for a spark to occur. With cylinder pressure, the higher the pressures in the cylinder (the result of high compression ratios and high boost levels), the more voltage required for a spark to occur.