6| Mazda 13B-REW
Mazda’s Turbocharged Rotary says, “No Pistons, No Problem”…
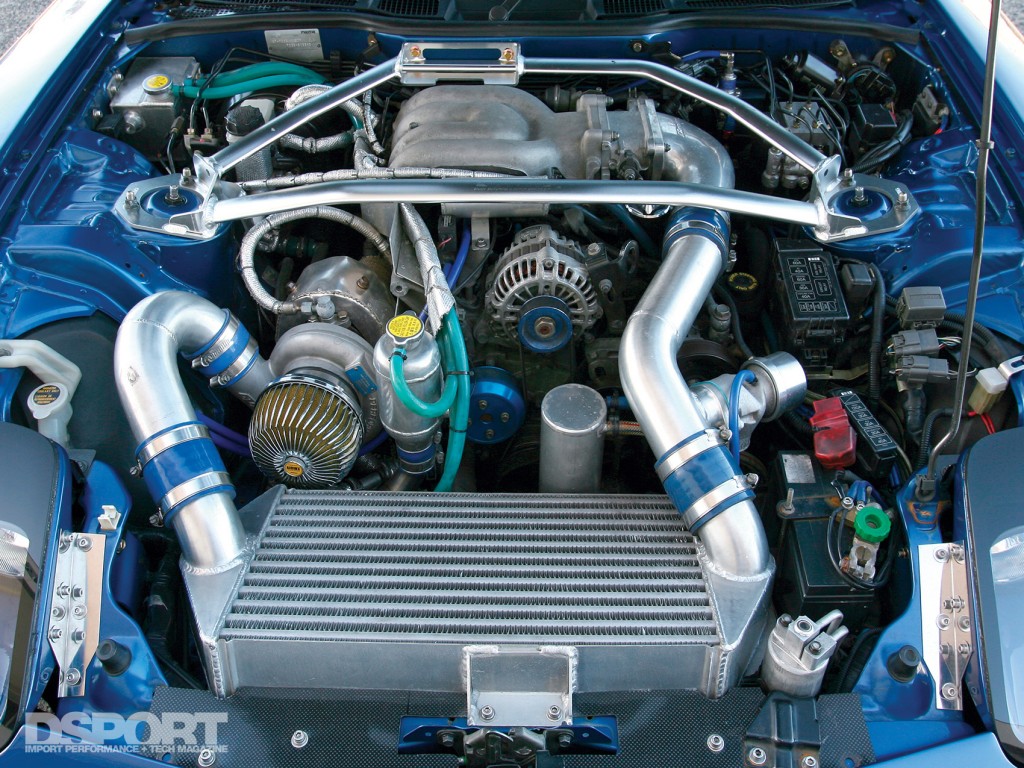
The only non-piston combustion engine on the market happens to offer tremendous power potential and high specific output, putting the turbocharged Mazda 13B-REW in the sixth spot on the list. Mazda is the only manufacturer to invest and put into mass production rotary engines for passenger cars, and the turbocharged 13B-REW earned recognition for propelling the Mazda RX7 FD3S. The lightweight, low profile rotary engine design allows the engine to sit low and behind the front wheels, helping to lower the center of gravity. This was one of the great features of the rotary engine that aided in the handling prowess that the RX7 had come to be known for. There were 15 variants of rotary engines that preceded the 13B-REW. However, what set this engine apart was it’s the twin sequential turbochargers, high engine speeds and power output. The rotary’s high exhaust energy can drive massive turbochargers that help to raised performance even further. Its modular design makes increasing displacement possible by adding rotors and housings and employing a new eccentric shaft (the rotary equivalent of a crankshaft.) Despite its high output-per-liter, it is not without its shortcomings. The apex seals (likened to piston rings) are sensitive to detonation, it is fuel inefficient and spark plug life is dramatically shorter compared to piston engines. Nevertheless, rotaries continue to shine in motorsports, powering drag, drift and circuit cars around the globe. The 13B-REW powered professional drag racers like Abel Ibarra and Adam Saruwatari into Import Drag Racing’s spotlight in the 90s while D1GP drivers Youichi Imamura, Ryuji Miki and Masao Suenaga drifted the rotary platform into the 2000s. In SuperGT competition, RE Amemiya and its various sponsors campaigned rotary-powered RX7s up through the 2010 season.
Opinion
What’s Hot:
• Lightweight
• Modular design
• High output-per-liter
• No valvetrain to limit engine speed
• Porting accomplishes role of upgrading cams and headwork
• High exhaust energy drives massive turbochargers
• Small/compact engine can be positioned low for balance
• Plenty of aftermarket support
What’s Not: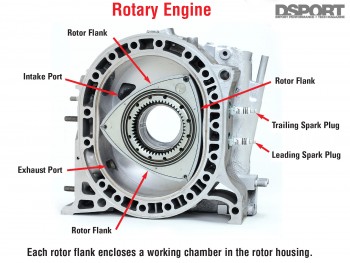
• Apex seals are sensitive to detonation
• Low displacement = low torque output
• High heat output from engine
• Limited spark plug life
• Not fuel efficient
• High fuel delivery demands
• High horsepower production demands carefully designed cooling system upgrades
SPEC SHEET
| ENGINE | |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer: | Mazda |
| Years In Production: | 1992-2002 |
| Engine Code: | 13B-REW |
| Displacement (cc): | 1,308cc |
| Peak Horsepower (@ RPM): | 255 bhp |
| Peak Torque (@ RPM): | 217 lb-ft |
| Rotor Material: | Steel |
| Rotor Housing Material: | Aluminum |
| Compression Ratio: | 9.0:1 |
| Rotor Side Housing: | Iron |
| Throttle Body: | Single |
| Fuel Injectors: | Side Feed, High Impedance |
| 850 cc/min (Primary x2), 550 cc/min (Secondary x2) | |
| Ignition System: | Distributor |
| Applications: | 1992-2002 Mazda RX7 (FD3S) |